Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 11 Pages, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Materials Transactions, 64(11), p.2553 - 2559, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We attempted to calculate the hydrogen trapping energies on the incoherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates and Mg
precipitates and Mg Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg
Si crystallites in aluminum alloys from first-principles calculations. Since the unit cell containing the incoherent interface does not satisfy the periodic boundary condition, resulting in a discontinuity of crystal blocks, the hydrogen trapping energy was calculated in a region far from the discontinuity (vacuum) region. We found considerable trapping energies for hydrogen atoms at the incoherent interfaces consisting of assumed atomistic arrangement. We also conducted preliminary calculations of the reduction in the cohesive energy by hydrogen trapping on the incoherent interfaces of Mg Si in the aluminum matrix.
Si in the aluminum matrix.
Ikeda, Yoichi*; Umemoto, Yoshihiko*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Hashimoto, Yuki*; Kitazawa, Takafumi*; Fujita, Masaki*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0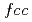 -base GdO
-base GdO precipitations in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloy
precipitations in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloyIto, Yuto*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(8), p.2022 - 2025, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have found that, during 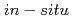 scanning transmission electron microscopy observations, heating of a Mg
scanning transmission electron microscopy observations, heating of a Mg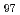 Zn
Zn Gd
Gd (at.%) alloy at 623K leads to dynamic precipitations of face-centered-cubic (
(at.%) alloy at 623K leads to dynamic precipitations of face-centered-cubic (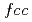 )-based Gd nanoparticles. With the aid of density-functional theory (DFT) calculations, the observed lattice constant of 5.32
)-based Gd nanoparticles. With the aid of density-functional theory (DFT) calculations, the observed lattice constant of 5.32 , which is larger than that expected for pure
, which is larger than that expected for pure 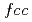 -Gd of 5.06
-Gd of 5.06 , is likely to be due to oxygen atoms inserted at tetrahedral interstitial sites with essentially a fractional occupation. Systematic DFT calculations show possible occurrences of
, is likely to be due to oxygen atoms inserted at tetrahedral interstitial sites with essentially a fractional occupation. Systematic DFT calculations show possible occurrences of 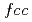 -Gd-based oxide phase with a wide non-stoichiometry range by occupying either tetrahedral or octahedral interstitial positions, being represented as GdO
-Gd-based oxide phase with a wide non-stoichiometry range by occupying either tetrahedral or octahedral interstitial positions, being represented as GdO .
.
Kurihara, Kensuke*; Lobzenko, I.; Tsuru, Tomohito; Serizawa, Ai*
Materials Transactions, 64(8), p.1930 - 1936, 2023/08
Nanoclusters formed in Al-Mg-Si alloys affect the aging behavior of the alloys depending on the formation temperature. In the present study, first-principles calculations were carried out to evaluate the two- and three-body interactions between Mg, Si atoms and vacancies in the Al matrix and estimate the effect of local bonding on the formation of nanoclusters. Monte Carlo simulations were subsequently performed to investigate the stable structure of the nanocluster formed in Al-0.95 mass pct Mg-0.81 mass pct Si alloy. We found that the Mg-Si and Si-Vac pairs are stable in the Al matrix. The result shows that the solute atoms easily aggregate with different types of solute atoms and that the Si atom has a strong attractive interaction with a vacancy. Furthermore, Mg-Si-vacancy three-body clusters is more stable than Mg-Si and Si-vacancy pairs in the Al matrix. The nanoclusters in the Al matrix were thermally stabilized by the stable configurations between solute atoms and vacancy. Thus, the electronic structure calculations suggested that the local bondings within a nanocluster play a significant role in not only the thermal stability but also the formation and growth behavior of nanoclusters during aging at low temperatures.
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
Urakawa, Yutaka*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(5), p.1065 - 1071, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Yohei*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Miyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Terauchi, Masami*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(5), p.950 - 954, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dilute Mg-Zn-Y alloy with a mille-feuille structure (MFS) exhibits a mechanical strength comparable to Mg-Zn-Y alloy with long period stacking/ordered (LPSO) structure through kink deformation. In order to deepen understanding the thermal stability of the MFS-type Mg alloys, it is required to clarify the solute cluster structures composed of Zn and Y in solute enriched stacking faults (SESFs). In this study, electron energy-loss and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy based on scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM-EELS/EDS) were conducted to investigate the electronic structure and composition of Zn and Y in the SESFs of the MFS-Mg alloy. Zn-L2,3 spectra indicated that the valence charges of Zn in the dilute Mg alloy were different from that of the LPSO-type Mg-Zn-Y alloy. In addition, the intensity ratio of L3/L2 in Y-L2,3 spectrum of the dilute MFS-Mg alloy was larger than that of the LPSO-Mg alloy, reflecting the electron occupancies of 4d3/2 and 4d5/2 orbitals of Y atoms were different from those of the LPSO-Mg alloys. STEM-EELS analysis of the SESF composition in the dilute MFS-Mg alloy indicated that the Zn/Y ratio should be lower than that of the LPSO-Mg alloy, which was confirmed also by STEM-EDS measurements. These results indicate that the cluster structure in the SESFs of the dilute MFS-Mg alloy should be different from the ideal Zn6Y8 cluster in the LPSO-type Mg-Zn-Y alloys.
Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Egusa, Daisuke*; Abe, Eiji*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.813 - 816, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by
Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by  neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionHarjo, S.; Gong, W.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Kawamura, Yoshihito*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.766 - 773, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sasaki, Hirokazu*; Akiya, Shunta*; Oba, Yojiro; Onuma, Masato*; Giddings, A. D.*; Okubo, Tadakatsu*
Materials Transactions, 63(10), p.1384 - 1389, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.538 - 544, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The time dependence of the corrosion behavior of tantalum (Ta), which is used in nuclear fuel reprocessing equipment, in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions was investigated by immersion tests, and the mechanism of the time dependence was examined via surface observations and electrochemical measurements. The immersion tests were conducted at room temperature with NaOH concentrations ranging from 1 to 7 mol/L for immersion periods of 24 to 168 h. The corrosion rate increased with the NaOH concentration but peaked with the immersion period and then decreased. The time to peak of the corrosion rate was shorter with higher NaOH concentration. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and Raman spectra of the surfaces of the specimens immersed in the 7 mol/L NaOH solution for more than 48 h showed Na Ta
Ta O
O formation. The polarization resistance decreased with immersion time for all NaOH concentrations up to about 24 h after immersion. Thereafter, the polarization resistance increased with immersion time in 7 mol/L NaOH solution and remained almost constant in the other NaOH concentrations. Findings suggested that the change in the corrosion rate was affected by the film formation during immersion, since the time dependence of the polarization resistance and the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance had the same tendencies. The precipitation film was mainly Na
formation. The polarization resistance decreased with immersion time for all NaOH concentrations up to about 24 h after immersion. Thereafter, the polarization resistance increased with immersion time in 7 mol/L NaOH solution and remained almost constant in the other NaOH concentrations. Findings suggested that the change in the corrosion rate was affected by the film formation during immersion, since the time dependence of the polarization resistance and the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance had the same tendencies. The precipitation film was mainly Na Ta
Ta O
O formed by the dissolution of the passivity film on Ta.
formed by the dissolution of the passivity film on Ta.
 TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloy
TEM observation and MD simulation of frank partial dislocation climbing in Al-Cu alloyChen, J.*; Yoshida, Kenta*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Shimada, Yusuke*; Inoue, Koji*; Konno, Toyohiko*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.468 - 474, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In situ electron irradiation using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) was performed to visualize the Frank loop evolution in aluminium-copper (Al-Cu) alloy with an atomic-scale spatial resolution of 0.12 nm. The  HRTEM observation along the [110] direction of the FCC-Al lattice, Frank partial dislocation bounding an intrinsic stacking fault exhibited an asymmetrical climb along the
HRTEM observation along the [110] direction of the FCC-Al lattice, Frank partial dislocation bounding an intrinsic stacking fault exhibited an asymmetrical climb along the  112
112 direction opposed to those in the reference pure Al under an electron irradiation, with a corresponding displacement-per-atom rate of 0.055-0.120 dpa/s. The asymmetrical climb of the partial dislocation was described as pinning effects due to Cu-Cu bonding in Guinier-Preston zones by a molecular dynamics simulation.
direction opposed to those in the reference pure Al under an electron irradiation, with a corresponding displacement-per-atom rate of 0.055-0.120 dpa/s. The asymmetrical climb of the partial dislocation was described as pinning effects due to Cu-Cu bonding in Guinier-Preston zones by a molecular dynamics simulation.
Saito, Junichi; Kobayashi, Yohei*; Shibutani, Hideo*
Materials Transactions, 62(10), p.1524 - 1532, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji; Ukai, Shigeharu*
Materials Transactions, 62(8), p.1239 - 1246, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The FeCrAl-ODS alloy claddings were manufactured and Vickers hardness, ring tensile tests and TEM observations of these claddings were performed to investigate the effects of thermal aging at 450  C for 5,000 and 15,000 h. The age-hardening of all FeCrAl-ODS alloy cladding was found. In addition, the significant increase in tensile strength was accompanied by much larger loss of ductility. It was suggested that this age-hardening behavior was attributed to the (Ti, Al)-enriched phase (
C for 5,000 and 15,000 h. The age-hardening of all FeCrAl-ODS alloy cladding was found. In addition, the significant increase in tensile strength was accompanied by much larger loss of ductility. It was suggested that this age-hardening behavior was attributed to the (Ti, Al)-enriched phase ( ' phase) and the
' phase) and the  ' phase precipitates (content of Al is
' phase precipitates (content of Al is  7 wt%). In comparison with FeCrAl-ODS alloys with almost same chemical compositions, there was significant age-hardening in both alloys. However, the extrusion bar with no-recrystallized structures was keeping good ductility. It was suggested that this different behavior of reduction ductility was attributed to the effects of grain boundaries, dislocation densities and specimen preparation direction.
7 wt%). In comparison with FeCrAl-ODS alloys with almost same chemical compositions, there was significant age-hardening in both alloys. However, the extrusion bar with no-recrystallized structures was keeping good ductility. It was suggested that this different behavior of reduction ductility was attributed to the effects of grain boundaries, dislocation densities and specimen preparation direction.
Zhao, C.*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nishitani, Shigeto*; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Materials Transactions, 62(7), p.929 - 934, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in measuring the diffusion coefficient of Cu in Fe in a low temperature range that had not been measured so far. Since the diffusion couple, which is a general method for measuring the diffusion coefficient, can be applied only at high temperature, atom probe tomography and Cu precipitation rate theory were used in this study. The estimated diffusion coefficient was found to be more reliable than that obtained in previous studies. Therefore, it is considered that the estimation by the atom probe provided higher accuracy. Furthermore, the kinetic Monte Carlo simulation revealed that the diffusion coefficient estimated by this method tends to be slightly overestimated as the temperature decreases.
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Materials Transactions, 62(6), p.763 - 769, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, the iron rust layer formed on the low alloy steel under air-solution alternating conditions was investigated by cross-sectional observation and analysis, and the mechanism of the accelerated corrosion of the steel under alternating conditions was clarified. The observations and analysis showed that the multilayered iron rust layer composed of the red rust layer (FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe O
O ), inner crystal (Fe
), inner crystal (Fe O
O ), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multilayered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of dissolved oxygen under alternating conditions. This acceleration is the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel under alternating conditions was accelerated.
), and inner rust layer was formed on the low alloy steel. It can be considered that the multilayered iron rust layer accelerated the cathodic reaction rate of dissolved oxygen under alternating conditions. This acceleration is the reason why the corrosion rate of the low alloy steel under alternating conditions was accelerated.
Otani, Kyohei; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Materials Transactions, 62(6), p.815 - 820, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The synergistic effects of metal cations in a solution on the ability of sodium gluconate to inhibit the corrosion of mild steel were investigated quantitatively focus on the parameter Y, which represents the "corrosion inhibitory effect of cations" by immersion and electrochemical tests. The results of the investigations showed that the inhibition ability of gluconates improved with increasing Y value of the metal cations in model freshwater. The electrochemical and surface analyses indicated that gluconate ligands and large-Y metal cations formed a protective film with few defects on the mild steel.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi
Materials Transactions, 62(5), p.582 - 589, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English